What Book Value Means to Investors
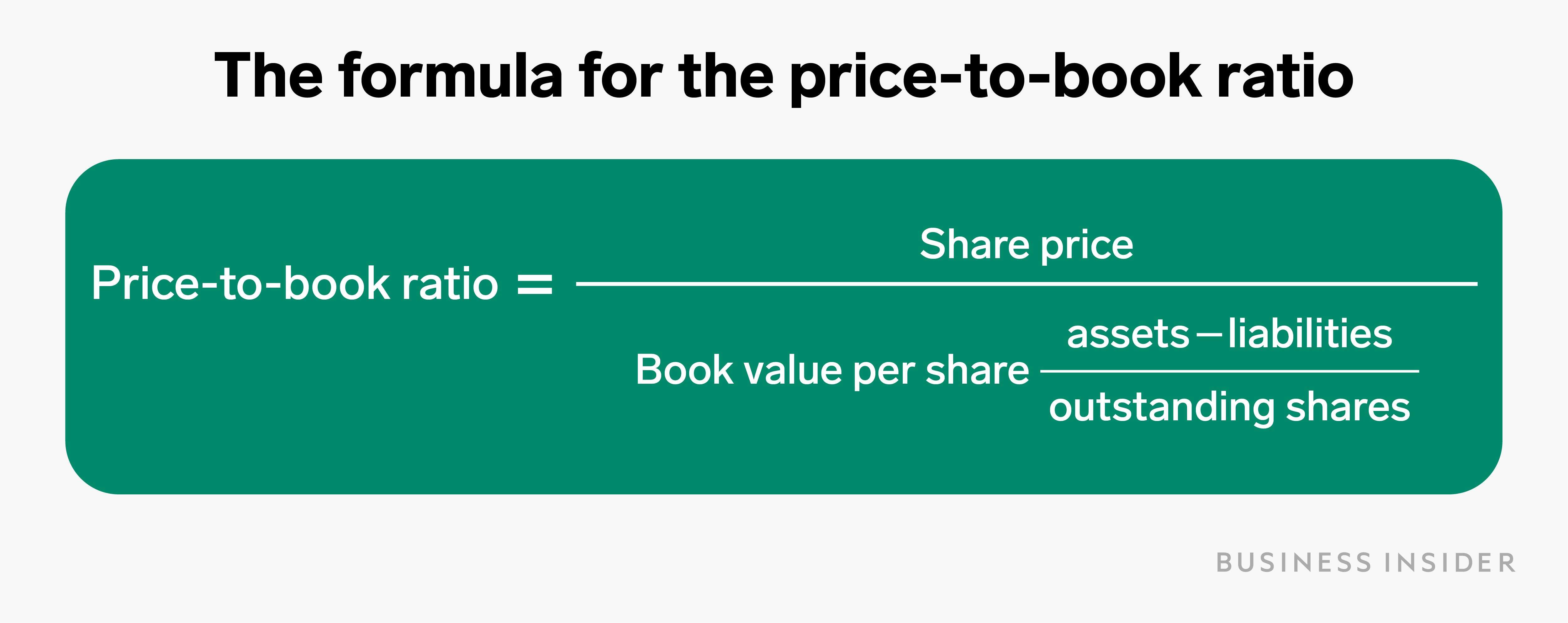
Despite the increase in share price (and market capitalization), the book value of equity per share (BVPS) remained unchanged in Year 1 and 2. The formula for BVPS involves taking the book value of equity and dividing that figure by the weighted average of shares outstanding. A P/B ratio of 1.0 indicates that the market price of a share of stock is exactly equal to its book value. For value investors, this may signal a good buy since the market price generally carries some premium over book value.
How often is BVPS calculated?
Let’s say that Company A has $12 million in stockholders’ equity, $2 million of preferred stock, and an average of 2,500,000 shares outstanding. You can use the book value per share formula to help calculate the book value per share of the company. To calculate book value per share, simply divide a company’s total common equity by the number of shares outstanding. For example, if a company has total common equity of $1,000,000 and 1,000,000 shares outstanding, then its book value per share would be $1. The figure that represents book value is the sum of all of the line item amounts in the shareholders’ equity section on a company’s balance sheet.
Formula to Calculate Book Value of a Company
While this dip in earnings may drop the value of the company in the short term, it creates long-term book value because the company’s equipment is worth more and the costs have already been discounted. The answer could be that the market is unfairly battering the company, but it’s equally probable that the stated book value does not represent the real value of the assets. Companies account for their assets in different ways in different industries, and sometimes even within the same industry. A price-to-book ratio under 1.0 typically indicates an undervalued stock, although some value investors may set different thresholds such as less than 3.0. Even though book value per share isn’t perfect, it’s still a useful metric to keep in mind when you’re analyzing potential investments.
The Formula for Book Value Per Common Share Is:
Although infrequent, many value investors will see a book value of equity per share below the market share price as a “buy” signal. But an important point to understand is that these investors view this simply as a sign that the company is potentially undervalued, not that the fundamentals of the company are necessarily strong. Because book value per share only considers the book value, it fails to incorporate other intangible factors that may increase the market value of a company’s shares, even upon liquidation.
Book Value Per Share vs. Market Stock Price: What is the Difference?
- While Book Value Per Share can be a helpful indicator of a company’s tangible net assets, it has several limitations that investors should be aware of.
- This is because preferred stockholders are ranked differently than common stockholders in the event the company is liquidated.
- This means that, in the worst-case scenario of bankruptcy, the company’s assets will be sold off and the investor will still make a profit.
- But be sure to remember that the book value per share is not the only metric that you should consider when making an investment decision.
To get the book value, you must subtract all those liabilities from the company’s total assets. The book value per share (BVPS) is a ratio that weighs stockholders’ working at xerox in amsterdam total equity against the number of shares outstanding. In other words, this measures a company’s total assets, minus its total liabilities, on a per-share basis.
Online Investments
Now, let’s say that the company invests in a new piece of equipment that costs $500,000. The book value per share would still be $1 even though the company’s assets have increased in value. For example, let’s say that ABC Corporation has total equity of $1,000,000 and 1,000,000 shares outstanding. This means that each share of stock would be worth $1 if the company got liquidated. If a company’s BVPS is higher than its market value per share (the current stock price), the stock may be considered undervalued. This situation suggests a potential buying opportunity, as the market may be undervaluing the company’s actual worth.
Earnings, debt, and assets are the building blocks of any public company’s financial statements. For the purpose of disclosure, companies break these three elements into more refined figures for investors to examine. Investors can calculate valuation ratios from these to make it easier to compare companies. Among these, the book value and the price-to-book ratio (P/B ratio) are staples for value investors. The Book Value Per Share provides information about how the value of a company’s stock compares to the current Market Value Per Share (MVPS), or current stock price.
The following image shows Coca-Cola’s “Equity Attributable to Shareowners” line at the bottom of its Shareowners’ Equity section. In this case, that total of $24.1 billion would be the book value of Coca-Cola. It’s one metric that an investor may look for if they’re interested in valuating Coca-Cola as a potential investment. Also, we can add Equity Share capital and Reserves to get shareholder’s equity which is 5,922 cr + 2,87,569 cr, which will sum to 2,93,491 cr.

This tells you something about book value as well as the character of the company and its management. You won’t get this information from the P/B ratio, but it is one of the main benefits of digging into the book value numbers and is well worth the time. An investor looking to make a book value play has to be aware of any claims on the assets, especially if the company is a bankruptcy candidate. Usually, links between assets and debts are clear, but this information can sometimes be played down or hidden in the footnotes. Like a person securing a car loan by using their house as collateral, a company might use valuable assets to secure loans when it is struggling financially.
Clear differences between the book value and market value of equity can occur, which happens more often than not for the vast majority of companies. Alternatively, another method to increase the BVPS is via share repurchases (i.e. buybacks) from existing shareholders. If relevant, the value of preferred equity claims should also be subtracted from the numerator, the book value of equity. The term “book value” is derived from accounting lingo, where the accounting journal and ledger are known as a company’s books. To better understand book value per share, it helps to break down each aspect of the ratio. If a company is selling 15% below book value, but it takes several years for the price to catch up, then you might have been better off with a 5% bond.












